The sputum smear slides of which were acquired images to the data base were used as controls for staining of the project "Evaluation of alternative dyes for diagnosing Tuberculosis" held from 2008 to 2010, which was approved, without restrictions, under protocol number 186/08 by the Ethics Committee on Human Research – CEP/INPA (National Institute for Research in the Amazon),
The sputum samples are from patients suspected of pulmonary TB.
Kinyoun stain was the method of staining used. It is similar to the Ziehl-Neelsen stain, but does not involve heating the slides being stained.
Two types of database were composed:
Image database 1: Out-of-focus-blur-evaluation (TB_IMAGE_DB_FOCUS.V1)
It is known that out-of-focus image is one of the important factors which may influence tasks of detection and recognition. To investigate the effect of out-of-focus blur on the performance of bacillus detection system, an image database was built. From each field from sputum smear 10 images were acquired with different focal lengths. The step of focal-length was 2,5μm.
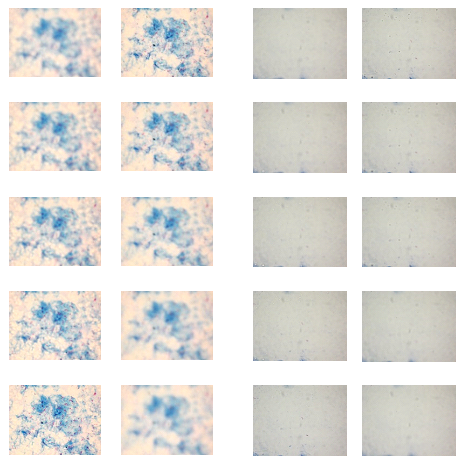
Figure 1: Examples of two set of microscopy images (ten images were acquired with different focal lengths to each set).
Image database 2: bacilli-detection-evaluation (TB_IMAGE_DB_BACILLI.V1)
This image database is intended to enable performance comparison between algorithms and techniques for detection and recognition of bacilli. It comprises 120 images which were obtained from sputum smear microscopy slices of 12 patients (10 fields for each patient).
Based on the background content, the database is divided in two groups. Group 1 consists of images with high density of background content (HDB). Group 2 consists of images with low density of background content (LDB). The HDB group is characterized by a strong presence of counterstain with methylene blue solution in the background, while the LDB group is characterized by a weak presence of this same counterstain(see examples in figure 2).
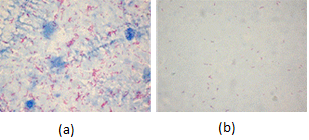
Figure. 2. (a) Image with high density of background content. (b) Image with low density of background content
In all the 120 images, the identified objects were enclosed within a geometric shape by a specialist. A true bacillus was enclosed in a circle. An agglomerated bacillus was enclosed by a rectangle and a doubtful bacillus (the image focus or geometry does not allow a clear identification of the object) was enclosed by a polygon. The images with marked objects could be used as gold standard to evaluate the accuracy; sensitivity and specificity of bacilli recognition (see examples in figure 3).
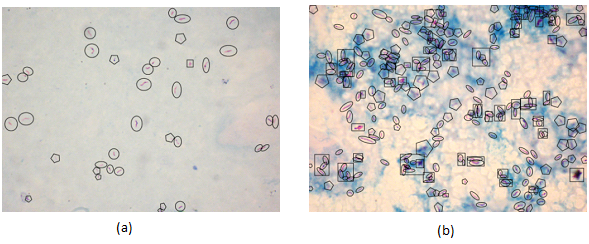
Figure 3. Examples of images with artefacts identified by specialist (a) LDB image (b) HDB image (Circle – true bacillus; Polygon – doubtful bacillus; rectangle – agglomerated bacilli)

